Table of Content
▲- Why Is the Agra Gwalior Expressway Important?
- Agra Gwalior Expressway Quick Facts
- Route Map of the Agra Gwalior Expressway
- Project Status and Timeline
- Facilities and Features Along the Expressway
- Social and Economic Impact of the Expressway
- Real Estate Impact of the Agra Gwalior Expressway
- Tenders and Contractors
- Agra Gwalior Expressway: Travel Time Benefits
- Agra Gwalior Expressway Village List
- Conclusion
The Agra Gwalior Expressway is a proposed 88.4 km-long, six-lane, access-controlled greenfield highway designed to dramatically reduce travel times between Agra and Gwalior. Currently, the journey takes 2–3 hours; once operational, it is expected to take only one hour, with Delhi to Gwalior reduced to just four hours. This expressway is a vital infrastructure project for northern India, aiming to boost connectivity, economic growth, and regional development.
Why Is the Agra Gwalior Expressway Important?
Key Benefits:
- Reduced Travel Time: Agra to Gwalior in 1 hour; Delhi to Gwalior in 4 hours.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Links to Delhi-Mumbai Expressway, Agra-Lucknow Expressway, and Bundelkhand Expressway.
- Boost to Tourism & Economy: Faster travel attracts tourists and investors.
- Real Estate Growth: Expected appreciation in property values along the corridor.
- Employment Opportunities: Both during construction and post-completion commercial activity.
Example: Commuters currently face congestion on NH-44 and the Agra-Delhi Highway. The new expressway will offer a faster, more reliable alternative.
Also Read: UP to link Agra-Lucknow Expressway to Purvanchal Expressway
Agra Gwalior Expressway Quick Facts
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Total Length |
88.40 km |
|
Lanes |
6 |
|
Estimated Cost |
₹4,612.65 crore |
|
Owner |
NHAI (National Highways Authority of India) |
|
Status |
DPR prepared, land acquisition underway |
|
Project Model |
EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) |
|
Expected Completion |
2028 |
Route Map of the Agra Gwalior Expressway
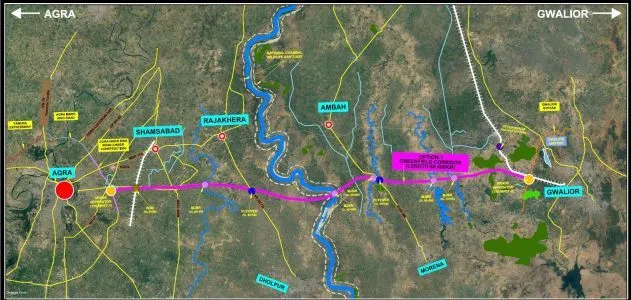
The expressway will start from Deri village, Agra, near the Inner Ring Road, and terminate at Susera village, near Gwalior bypass. It runs parallel to the Chambal River, connecting key towns:
- Uttar Pradesh: Nanawa, Etawah, Dholpur, Rohta, Shijroli
- Rajasthan: Seemalya, Bamor, Jajau
- Madhya Pradesh: Gwalior, Morena, Bhind, Shivpuri
The expressway also connects major national highways, linking:
- Delhi-Mumbai Expressway at Kota
- Agra-Lucknow Expressway at Deri, Agra
- Bundelkhand Expressway in Etawah
Impact: The expressway reduces congestion on existing roads, providing a faster, direct, and safer travel route.
Project Status and Timeline
Current Status (January 2026)
- DPR completed
- Land acquisition underway
- Construction expected to start by November 2025
- Targeted completion by 2028
- Estimated construction cost: ₹4,613 crore
Construction Details:
- Greenfield six-lane highway: Agra (Deri village) to Gwalior (Susera village)
- Safety and capacity upgrades on NH-44 between km 1058–1148
- Contractor: GR Infraprojects Ltd. (DBFOT model)
Travel Impact: Reduces the Agra-Gwalior journey from 2–3 hours to ~1 hour.
Facilities and Features Along the Expressway
- Petrol and electric vehicle charging stations
- Large food malls and rest areas
- Landscaping for better commuter experience
- Interchanges connecting to other major highways
Example: Commuters traveling from Delhi to Gwalior will now bypass congested routes, making travel more predictable and comfortable.
Social and Economic Impact of the Expressway
Employment Generation
- ~800 direct jobs during construction, with priority for local labor
- Post-construction: employment via industrial and commercial corridors
Real Estate Appreciation
- Improved connectivity will attract residential and commercial projects
- Ribbon development expected along the corridor, boosting property prices
Local Business Benefits
- Increased footfall and traveler numbers will help local vendors
- Growth in hospitality, retail, and logistics sectors
Example: Towns like Morena, Bhind, and Shivpuri are expected to witness significant commercial development and increased investment.
Real Estate Impact of the Agra Gwalior Expressway
The Agra Gwalior Expressway is projected to have a substantial influence on the real estate sector along its corridor:
- Residential Development: Areas near interchanges and major towns will see a rise in new housing projects.
- Commercial Growth: Retail, logistics, and hospitality spaces will expand due to increased commuter traffic.
- Property Value Appreciation: Improved accessibility and infrastructure upgrades will push up land and property prices.
- Investor Interest: Developers and investors are likely to focus on towns along the expressway for high ROI projects.
- Urban Expansion: Smaller towns along the route may experience rapid urbanization, with new amenities, schools, and healthcare facilities emerging.
Example: Morena and Bhind are expected to see a 15–20% increase in residential property demand within 2–3 years of expressway completion.
Tenders and Contractors
- Initially divided into 3 packages (2023) – later reshaped into a single DBFOT contract (January 2024)
- GR Infraprojects Ltd. selected in March 2025
- EPC model: Design, Build, Finance, Operate, Transfer
- Project includes NH-44 upgrades for safety and traffic flow
Also Read: Lucknow Kanpur Expressway: Route, Map, Travel Time, and Key Details
Agra Gwalior Expressway: Travel Time Benefits
|
Route |
Current Time |
Expected Time |
|
Agra – Gwalior |
2–3 hours |
1 hour |
|
Delhi – Gwalior |
6–7 hours |
4 hours |
Impact: Faster travel improves logistics, tourism, and regional trade.
Agra Gwalior Expressway Village List
Uttar Pradesh
Rohta, Shijroli, Masoodpur, Nagal Makrol, Baragaon, Gopalpura, Kakua, Ladampur, Sikrauda, Bad, Mania, Morena, Usra, Edalpur, Chonda, Tehra, Dholpur, Naurabad, Saiyan
Rajasthan
Bamor, Jajau
Madhya Pradesh
Gwalior, Bhind, Shivpuri
Conclusion
The Agra Gwalior Expressway is set to transform connectivity in northern India by reducing travel times, enhancing regional trade, and promoting economic growth. The 88.4 km six-lane greenfield expressway will create employment, improve logistics, and boost real estate values in towns along its route. With modern facilities like EV charging stations, food malls, and landscaped rest areas, the expressway promises a safer and more comfortable journey for commuters. This landmark project underlines India’s commitment to high-speed, infrastructure-driven regional development.






_1771582392.webp)
_1771577585.webp)
Ans 1. The Agra Gwalior Expressway is an 88.4 km-long, six-lane, access-controlled greenfield highway designed to reduce travel time between Agra and Gwalior from 2–3 hours to just 1 hour.
Ans 2. It improves connectivity in northern India, boosts tourism, supports regional trade, generates employment, and is expected to increase real estate values along the corridor.
Ans 3. The project is expected to be completed by 2028.
Ans 4. The estimated construction cost is ₹4,612.65 crore.
Ans 5. The expressway connects key towns in Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh, including Nanawa, Etawah, Dholpur, Rohta, Shijroli, Bamor, Jajau, Gwalior, Morena, Bhind, and Shivpuri.
Ans 6. Agra to Gwalior travel will reduce from 2–3 hours to 1 hour, and Delhi to Gwalior travel will reduce from 6–7 hours to approximately 4 hours.
Ans 7. Facilities include petrol and electric vehicle charging stations, food malls, rest areas, landscaped zones, and interchanges connecting other major highways.
Ans 8. Improved connectivity is expected to drive residential and commercial development, increase property values, and attract investors along the corridor.
Ans 9. GR Infraprojects Ltd. has been selected under the EPC/DBFOT model to design, build, finance, operate, and transfer the expressway.
Ans 10. It will link the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway at Kota, the Agra-Lucknow Expressway at Deri, Agra, and the Bundelkhand Expressway in Etawah.
Ans 11. It will generate ~800 direct construction jobs, create commercial opportunities along the corridor, increase traveler footfall, and boost sectors like hospitality, retail, and logistics.
Ans 12. It passes through Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.