Table of Content
▲
Latest Update: Gift Deed
December 2022: Gift Deed must incorporate Maintenance Clause
In a recent ruling, the Supreme Court of India has stated that parents who gift their property in exchange for care must include a maintenance clause in the Gift Deed. Without such a provision, the Gift Deed becomes irrevocable, even if the children fail to care for the parents in old age.
In numerous instances, elderly parents resort to tribunals to invoke the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007. The Supreme Court's recent guidance specifically pertains to the inclusion of a maintenance clause in Gift Deeds.
Many situations arise where parents, out of affection, gift their properties to their children but are unable to revoke the gift due to the absence of a maintenance clause in the Gift Deed.
What is a gift deed?
A Gift Deed is a legal document by which an individual willingly transfers ownership of a movable or immovable property to another person. This document serves to reduce the likelihood of disputes in cases of property inheritance. The registration of a Gift Deed incurs charges determined by the state government. The subject of the gift can be either movable or immovable property. In matters of succession, a Gift Deed holds significance, distinguishing itself from a valid 'Will' created by the property owner.
In contrast to a Will, a Gift Deed is immediately enforceable, requiring no court intervention for execution. Consequently, a Gift Deed offers a time-saving alternative to settling matters through a will. In the context of a Gift Deed, the individual making the gift is referred to as the Donor, while the recipient is termed the 'Donee.'
Properties that can be transferred through a Gift Deed

A Gift Deed is applicable for gifting both immovable and movable properties. In this context, immovable property encompasses anything affixed to the land or earth, excluding grass, growing crops, and standing timber. It is important to recognize that properties not falling within the classification of immovable properties are regarded as movable.
Gift Deed under the Transfer of Property Act
The Transfer of Property Act of 1882 governs the Gift Deed. According to the Act, a gift must be made without any monetary consideration, and the recipient (Donee) must formally accept the gift during the lifetime of the person making the gift (Donor). The effectiveness of a Gift Deed, under the Transfer of Property Act, is contingent upon its registration with the Registrar or Sub-registrar's office. Once registered, the transfer of property takes immediate effect.
The Transfer of Property Act explicitly outlines the conditions for the validity of a Gift Deed. According to the Act, a Gift Deed is considered valid only if -
- The property mentioned in the Gift Deed must exist when making the Gift.
- The Donor of the concerned property must be the lawful owner with a clear title.
- The Gift must be voluntary and without coercion.
- The Gift must not involve monetary/otherwise consideration
- The Donee must accept the Gifted property
Components of a Gift Deed
The Gift Deed contains several clauses and essential details which must be mentioned in the document. Several clauses mentioned in the Gift Deed are-
- Transfer at free will- The Gift Deed must explicitly mention that the transfer of the Gifted property is being done of the Donor's free will, and he/she is not under any pressure/threat to gift the property.
- Details of the Donor and Donee- The Gift Deed must contain the name, address, and relationship of the Donor and Donee.
- Consideration- The Gift Deed must explicitly mention that the Donor is gifting the property out of love towards the Donee and will not take any monetary consideration in exchange.
- Details of the property- The Gift Deed must contain the dimensions, plan, and area details of the property in question so that there remains no ambiguity later.
- Property Rights of the Donee- The Gift Deed must mention the property rights of the Donee. The gift deed clearly explains that the Donee can sell, lease, or rent the property as per his/her will. The Donee can also mortgage the property.
- Acceptance by the Donee- The Gift Deed must mention the acceptance of the gifted property by the Donee.
- Witnesses- As the execution of a Gift Deed requires the presence of two witnesses, the Gift Deed must mention the name and address of the witnesses. A valid Gift deed must be signed and attested by two witnesses.
- Revocation- It is advisable not to have a revocation clause in the Gift Deed as voluntary, and the ownership gets transferred to the Donee once the deed is executed.
How to Draft a Gift Deed?
You can use the following way to draft a gift deed:-
- The place and date should be mentioned at the top on which the gift deed is to be executed.
- Both parties should mention all relevant information like address, name, date of birth and signature.
- Mention the complete details of the property for which a deed is being done
- A gift deed should have two witnesses and their signatures.
- A gift deed should be printed on stamp paper once the amount is paid. Once that is done, it should be registered at the registrar’s or sub-registrar’s office.
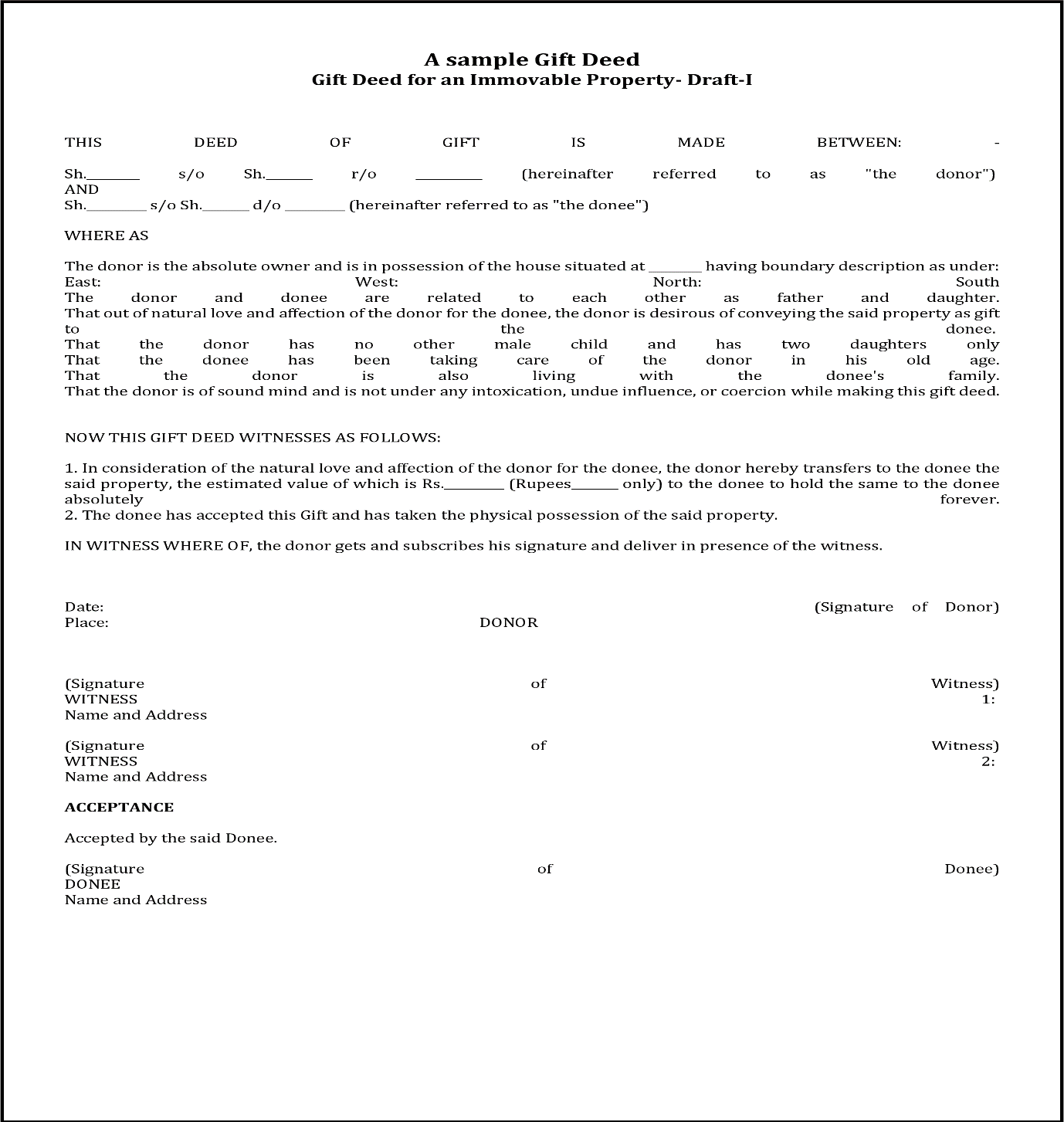
Gift Deed Format
A Gift Deed has a standard format. You can download a sample Gift Deed Format here.
Gift Deed Registration
In accordance with the Transfer of Property Act of 1882, a Gift Deed is deemed valid only when registered. The registration process entails the inclusion of the donor's and donee's signatures, along with attestation by two mandatory witnesses.
For the Gift Deed to be legally enforceable, it must undergo registration at the registrar's office. This registration involves detailing essential clauses on a stamp paper and payment of the applicable stamp duty, which varies from state to state. It is important to note that if the gifted asset is movable, the registrar's office jurisdiction is determined by the donor's place of residence.
Documents Required for Gift Deed Registration
Gift deed registration is done at the Registrar/Sub-registrar’s office. However, to register a Gift Deed, important identity documents and property documents are required, such as
- Original Gift Deed
- ID Proof like Aadhar Card, Driving License among others
- PAN Card of the donor and donee
- Document such as a sale deed or Title Deed to prove the ownership of the donor
- Passport size photograph
- ID proof of the witnesses
- Address proof of witnesses
Stamp duty on gift deed registration
Tax implications on the Gifts, and stamp duty on gift deed forms are an essential part of the Gift Deed registration. After April 2017, Gifts are taxed under Section 56 of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
According to the said Act, if a person receives a sum of more than Rs 50,000 as a gift, then the entire gift amount will be taxed under the head of ‘Income from Other Sources'.
Section 56 of the Income Tax Act specifies that when a person receives an immovable property as a Gift and the stamp duty charges exceed Rs 50,000, then the stamp duty value of the gift is taxable and will be paid by the Donee.
Stamp Duty on Gift Deeds in the Different States |
||
|
Sr No |
State |
Stamp duty on Gift Deed |
|
1 |
Haryana |
Rural Areas- 3% Urban Aras- 5% |
|
2 |
Delhi |
Men: 6% Women: 4% |
|
3 |
Gujarat |
4.9% of the market value |
|
4 |
Karnataka |
Family members: Rs 1,000- 5,000 Non-family: 5.6% of the land value (Including registration fee) |
|
5 |
Telangana |
Stamp duty is 5 % of the market value Registration Charges- 0.5 % of the market value |
|
6 |
Madhya Pradesh |
Family member- 2.5% of the market value of the property Non-family Member- 5% of the market value of the property |
|
7 |
Maharashtra |
Family members: 3% Other relatives: 5% Agricultural land/ residential property: Rs 200 |
|
8 |
Punjab |
For Family members: NIL For Non-family: 6% |
|
9 |
Rajasthan |
For Men: 5% Women: 3-4% SC/ST or BPL: 3% Widow: None To wife: 1% Immediate family: 2.5% |
|
10 |
Tamil Nadu |
For Family members: 1% For Non-family members: 7% |
|
11 |
Uttar Pradesh |
For Men: 7% For Women: 6% |
|
12 |
West Bengal |
For Family members: 0.5% For Non-family: 6% Above Rs 40 lakh: Surcharge of 1% |
However, stamp duty payment is exempted in certain cases.
How to cancel a Gift Deed? (Step-by-step)
A Gift Deed can be cancelled using the mentioned procedure.
Step 1: To revoke a Gift Deed, a petitioner will write a petition to the court. In this petition, the Donor will list the clauses for cancelling the Deed.
Step 2: Once a petition is filed, notices will be issued to the concerned parties, including the Donor and the donee.
Step 3: Once the hearing is scheduled, the petitioner will have to submit documents, evidence, records and other supporting documents to substantiate the case.
Step 4: The court will hear the arguments of both sides and weigh the evidence submitted.
Step 5: If the grounds of Gift are legitimate, the Deed can be revoked by the court.
Step 6: Once the court has passed the ruling cancelling the Gift Deed, the petitioner may approach the registration office where the Gift Deed was registered with the court ruling. The gift deed will be removed from the Registration office records.
Gift deed: What if Property is Gifted to an NGO?
Usually, stamp duty is not levied if a property is gifted to an NGO. However, an NGO must register it within four months of the property transaction. Also, please note that few NGOs are not allowed to receive property as a gift.
Gift Deed: If you want to gift property after demise?
If you want to give property after demise to anybody, you must ensure that you do it through a will. You can make the changes in your will if you want to.
Gift Deed: What if Gift Deed is not accepted?
In case a gift deed is not accepted by the recipient till the time the donor is alive, the gift deed is considered void.
Tax Exemptions on the Property as a Gift
Under the Income Tax Act of India, taxes will not be applicable if the property/amount is received from any of the following persons.
-
If the gift in question is received from relatives, or
-
If the gift is received on the marriage of the individual concerned (donee), or
-
If the gift is received under a will or by inheritance, or
-
If the gift is received in contemplation of the death of the donor, or
-
If the gift is received from a local authority, as defined under Section 10(20) of the Income Tax Act, or
-
If the gift is received from a university, charitable foundation, educational organization, medical institution, hospital, or trust, mentioned under Section 10(23C) of the Income Tax Act, or
-
If the gift is received from a trust or institution (Duly registered under Section 12A or 12AA), or
-
If the donee receives the gift from a trust established solely to benefit the individual’s relative.
Can a Gift Deedbe revoked?
Yes! A gift deed can be revoked. The revocation or cancellation of a Gift Deed is governed by Section 126 of the Transfer of Property Act 1882. According to this act, a gift deed can be revoked only under the following conditions-
-
When an agreement between a donor or a donee specifies clearly that the Gift Deed has to be revoked, the Gift Deed can not be revoked at the sole wish of the donor. The Gift Deed revoked solely on the donor's wish is null and void.
-
The gift deed can be revoked in any manner as that of contract cancellation, except on the grounds of non-payment or failure of consideration.
-
The gift deed can be revoked entirely or partially.
A gift deed cannot be revoked on the grounds mentioned above. It must be highlighted that in case of a donor’s death, his/her legal heirs can revoke the gift deed on his/her behalf.
Gift Deed Revocation by Mutual Agreement
In accordance with the mutual agreement between the Donor and Donee, a gift deed may be suspended in the event of occurrences beyond the Donor's control. It is imperative to explicitly state that, in the case of non-fulfillment of such conditions, the Donor retains the right to revoke the gift deed.
Alternatively, if a condition is absent from the Gift Deed but is outlined in a separate mutual agreement, forming an integral part of the gift transaction, such a condition remains enforceable and valid.
Furthermore, the annulment of a gift deed is not warranted unless it is based on misinterpretation, fraud, undue influence, or an onerous one. Unilateral cancellation is not permitted; instead, it must be contested in a court of law. The challenging party must establish that the execution was not acknowledged by the Donor and was carried out under fraudulent or misrepresented circumstances.
For instance:
Arun makes a gift of Rs. 15 lakh in favour of Rajiv, and from that, Arun reserves 2 lakh for himself with Rajiv’s asset for taking it back at his pleasure from the total figure. In such a situation, the gift of Rs 13 lakh is valid, but the Rs. 2 lakh gift is void. It will continue to belong to Arun. The law will consider that transfer of Rs. 2 Lakh wasn’t made at all.
Gift Deed vs Will: Know the Difference
Investing in property is a highly desirable investment option. Nevertheless, there may arise a situation where you wish to transfer ownership rights to someone else. There are three methods for transferring rights: selling the property, which necessitates a sale deed; gifting the property, requiring a gift deed; and creating a will, which is relevant while the testator is alive and takes effect after their death. Let's explore the distinctions between a Gift Deed and a Will.
|
Particulars |
Gift deed |
Will |
|
Time Period |
Gift deed is made when donor is alive and is functional for lifetime |
Will is operational only after death of property owner |
|
Revoked |
A gift can be revoked only under special circumstances |
Can be revoked nth times |
|
Registration |
It is mandatory to get gift deeds registered under Section 123 of Property Transfer Act and Section 17 of the Registration Act. |
Registering a will is not mandatory |
|
Charges |
Stamp duty and registration charges should be paid on gift deed |
No stamp duty and registration charges are incurred |
|
Act |
Gift deed falls under the umbrella of Income Tax Act |
Will is governed by the Succession law |
Bottom Line: Gift Deed
In conclusion, a Gift Deed is a formal document through which a donor voluntarily transfers ownership of a movable or immovable asset to another person. It is imperative that a Gift Deed be registered, and the registration process incurs payment of the necessary registration charges.
Also Read: Everything you need to know about GST in the real estate sector.







_1770976628.webp)

_1771582392.webp)
_1771577585.webp)
Ans 1. Gift deed is the document through which a person voluntarily gifts a movable/immovable property to a person
Ans 2. Yes, a registered gift deed is a legal document.
Ans 3. Yes, a gift deed can be cancelled on certain grounds.
Ans 4. Yes, a gifted property can be sold.
Ans 5. For immediate transfer of ownership, a Gift deed is better.
Ans 6. Yes, a gift deed can be challenged in a court of law.
Ans 7. Once registered, a gift deed can not be revoked unilaterally. It must have the signature and consent of the donee (receiver).
Ans 8. Donee (receiver) pays the stamp duty on the gift.