Table of Content
▲
One of the essential and widely utilized materials in building construction is bricks. Standard brick sizes are employed to construct masonry walls that are known for their strength and durability. Bricks have a lengthy history of being a popular choice in construction due to their cost-effectiveness and robust nature. Traditionally, construction bricks were crafted from clay soil. These small building units, often made from baked clay, are securely positioned using mortar—an adhesive mixture comprising cement, sand, and water. Here's a comprehensive guide to understanding the various sizes of bricks employed in construction.
Brick size: Dimensions of Indian bricks
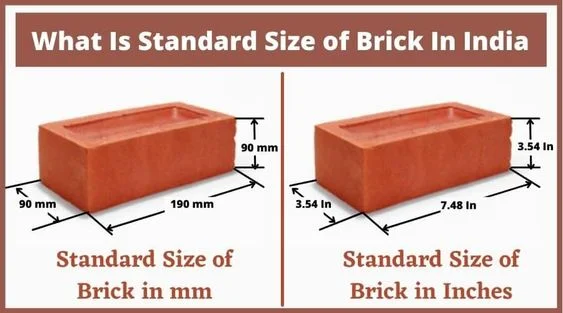
In India, bricks are typically used in one of four standard sizes.
- Modular/metric bricks: 190 x 90 x 90 mm. These bricks are made by machines.
- Non-modular bricks: 230 mm by 110 mm by 70 mm
- English size bricks: 230 x 115 x 75 mm, or 9 in. x 4.5 in. x 3 in. This is widely employed in India.
- Traditional bricks: 230 x 110 mm
Other dimensions based on the location exist as well. The bricks shouldn’t weigh more than 3 kg.
Brick size: Standard size and nominal size
In India, clay is burned in a kiln to create bricks.
- Bricks that are standard size are 190 x 90 x 90 mm without mortar.
- The nominal size is defined as 200 x 100 x 100 mm for bricks with mortar (10 mm).
Brick size in different parts of the world
| Country | Brick size |
| London | 215mm x 102.5mm x 65mm |
| USA | 194mm x 92mm x 57mm |
| Australia | 230mm x 110mm x 76mm |
| Romania | 240mm x 115mm x 63 |
| Russia | 250mm x 120mm x 62mm |
| Sweden | 250mm x 120mm x 62mm |
| South Africa | 222mm x 106mm x 73mm |
| Germany | 240mm x 115mm x 71mm |
| Denmark | 228mm x 108mm x 54mm |
| Bangladesh | 241mm x 114mm x 70mm |
Brick size: Different types of bricks
Following are some of the major types of bricks used in construction.
Sun-dried bricks

Unburnt bricks, also referred to as sun-dried bricks, represent the earliest and most basic form of bricks. The nomenclature of these bricks inherently describes the manufacturing process—they are not subjected to firing but are instead dried in the sun to achieve hardening. Commonly employed in rural regions or for temporary constructions, these bricks are suitable for short-term structures due to their reduced durability and lower resistance to fire and water.
Burnt clay bricks

Referred to as the "common brick," these bricks are the most widely utilized type in construction, finding application in major building projects such as foundations, walls, and columns. They are predominantly available in four distinct varieties:
- Superior bricks (best quality bricks)
- Low-quality bricks (moderate quality)
- Mediocre bricks (poor quality)
- Third-class bricks (over-burnt and in irregular shape)
Fly ash bricks

Designed exclusively for masonry purposes, these bricks incorporate either class C or class F fly ash, which is a by-product resulting from the combustion of coal and water at a temperature of 1000 degrees Celsius. Class C fly ash, recognized for its elevated calcium oxide content, is particularly well-suited for use in pillars, foundations, and walls. These bricks are commonly referred to as "self-cementing" bricks.
Concrete bricks

Produced by blending cement, sand, and water to form concrete, these bricks can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes. Concrete bricks are favored over clay bricks due to their ease of production directly at a construction site. This approach also reduces the amount of mortar required for the actual construction process.
Engineering bricks

These bricks find application in construction, valued for their strength, cold resistance, and fire resistance. They are commonly employed in basements where the demand for heightened chemical and water resistance exceeds standard requirements. Additionally, these bricks are known for their minimal porosity.
Fire bricks

Refractory bricks, also known as fire bricks, are crafted through a distinctive firing process. These bricks exhibit exceptional fire resistance, allowing them to endure extremely high temperatures without compromising their strength, shape, size, or properties. Consequently, they are extensively utilized in India, particularly in arid and rural regions. Refractory bricks are commonly employed in the lining of chimneys and furnaces, which typically experience elevated temperature levels.
Hollow bricks

As suggested by their name, these bricks are characterized by internal hollow spaces and weigh approximately one-third as much as standard bricks. They are alternatively referred to as cellular or cavity bricks. Due to their faster laying capability compared to regular bricks, they are commonly employed in expedited construction projects. Additionally, these bricks are often utilized in the construction of partitions.
Also Read: Popular Flooring Designs for Your Home (Cost, Pros & Cons Included)



_1773395099.webp)



Ans 1. Bricks are used in the wall’s construction because: Low price. It offers more strength. It is simple to build a wall using a different type of brick bond. Brick is easily manufactured nearby the construction site and is readily available.
Ans 2. The size of the brick will vary depending on national standards. The IS code 1077 of India refers to the standard brick size.
Ans 3. plural bricks or brick : a handy-sized unit of building or paving material typically being rectangular and about 2¹/₄ × 3³/₄ × 8 inches (57 × 95 × 203 millimeters) and made of moist clay hardened by heat. 2. : a good-hearted person. 3. : a rectangular compressed mass (as of ice cream)
Ans 4. In order to determine the specific number of bricks in 100 square feet, multiply the structure's square footage by 4.5. 100 X 4.5 = 450 bricks, so 450 bricks are required per 100 square feet for a 4.5-inch brick wall with a single layer.
Ans 5. An abundant natural resource, bricks are made from clay sediment called Varve Clay [vahrv kley], consisting of hydrated silicates of aluminum found in lake sediment and river beds. One of the oldest materials for building, architecture made with bricks have been dated back to 7,000 BC at archeological dig sites.